Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
🔍 Definition
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is defined as:
Abnormalities in kidney structure or function present for ≥3 months, with health implications.
✅ KDIGO 2012 Definition
CKD is present if either:
- GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m² for ≥3 months, with or without kidney damage
- Markers of kidney damage (even if GFR ≥60), e.g.:
- Albuminuria (UACR ≥30 mg/g)
- Urine sediment abnormalities
- Electrolyte abnormalities due to tubular disorders
- Histologic abnormalities
- Structural abnormalities (e.g., PKD)
- History of kidney transplantation
📊 CKD Staging: KDIGO 2012 GFR Categories
|
Stage |
GFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) |
Description |
|
G1 |
≥90 |
Normal or high (with evidence of damage) |
|
G2 |
60–89 |
Mildly decreased (with damage) |
|
G3a |
45–59 |
Mild–moderate ↓ |
|
G3b |
30–44 |
Moderate–severe ↓ |
|
G4 |
15–29 |
Severely ↓ |
|
G5 |
<15 |
Kidney failure (ESRD if dialysis-dependent) |
🧪 Albuminuria Categories (KDIGO)
|
Category |
UACR (mg/g) |
Description |
|
A1 |
<30 |
Normal–mild |
|
A2 |
30–300 |
Moderate (microalbuminuria) |
|
A3 |
>300 |
Severe (macroalbuminuria) |
✅ CKD is graded by GFR + albuminuria → used to stratify prognosis and progression risk
🔬 Pathophysiology
CKD involves progressive nephron loss, leading to:
- Compensatory hyperfiltration → glomerular hypertension → sclerosis
- Fibrosis from chronic inflammation
- Tubulointerstitial injury
- Activation of RAAS → systemic and glomerular HTN
- Uremic toxin accumulation → systemic effects
📉 Etiologies of CKD
|
Common Causes |
Examples |
|
Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1/2) |
Diabetic nephropathy |
|
Hypertension |
Hypertensive nephrosclerosis |
|
Glomerular diseases |
IgA nephropathy, FSGS, lupus nephritis |
|
Tubulointerstitial disease |
Chronic pyelonephritis, drug-induced |
|
Cystic diseases |
ADPKD |
|
Obstructive uropathy |
Stones, BPH, tumors |
|
Vascular diseases |
Renal artery stenosis, atheroemboli |
🧾 Clinical Features
|
System |
Manifestations |
|
Renal |
Polyuria (early), oliguria (late), hematuria, foamy urine |
|
Metabolic |
Acidosis, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia |
|
CVS |
HTN, LVH, pericarditis, CAD |
|
Hematologic |
Normocytic anemia (↓ EPO), platelet dysfunction |
|
GI |
Anorexia, N/V, uremic gastritis |
|
Neuro |
Encephalopathy, peripheral neuropathy, restless legs |
|
Derm |
Pruritus, uremic frost |
|
Bone |
CKD-MBD (renal osteodystrophy) |
🔍 Investigations
|
Modality |
Purpose |
|
Serum Creatinine, eGFR |
Kidney function |
|
UACR or 24-h protein |
Albuminuria grading |
|
USG KUB |
Kidney size, echogenicity, obstruction |
|
CBC |
Anemia |
|
Ca, Phos, PTH |
Bone–mineral axis |
|
ABG |
Metabolic acidosis |
|
Renal biopsy |
When diagnosis unclear or glomerular disease suspected |
💊 Drug Dosing in CKD (General Rules)
|
Drug Type |
Action |
|
Avoid |
NSAIDs, metformin (if GFR <30), contrast (if possible) |
|
Reduce dose |
Aminoglycosides, digoxin, vancomycin, LMWH |
|
Safe |
β-lactams (with adjustment), acetaminophen |
|
Monitor |
Electrolyte-altering drugs: ACEi/ARBs, spironolactone |
💉 Anemia in CKD
- Caused by ↓ EPO, chronic inflammation, blood loss
- Target Hb: 10–11.5 g/dL (not >13)
- Treatment:
- Epoetin alfa: 50–100 IU/kg 2–3x/week SC/IV
- Darbepoetin alfa: 0.45 mcg/kg weekly or biweekly
- Iron supplementation if ferritin <100 ng/mL or TSAT <20%
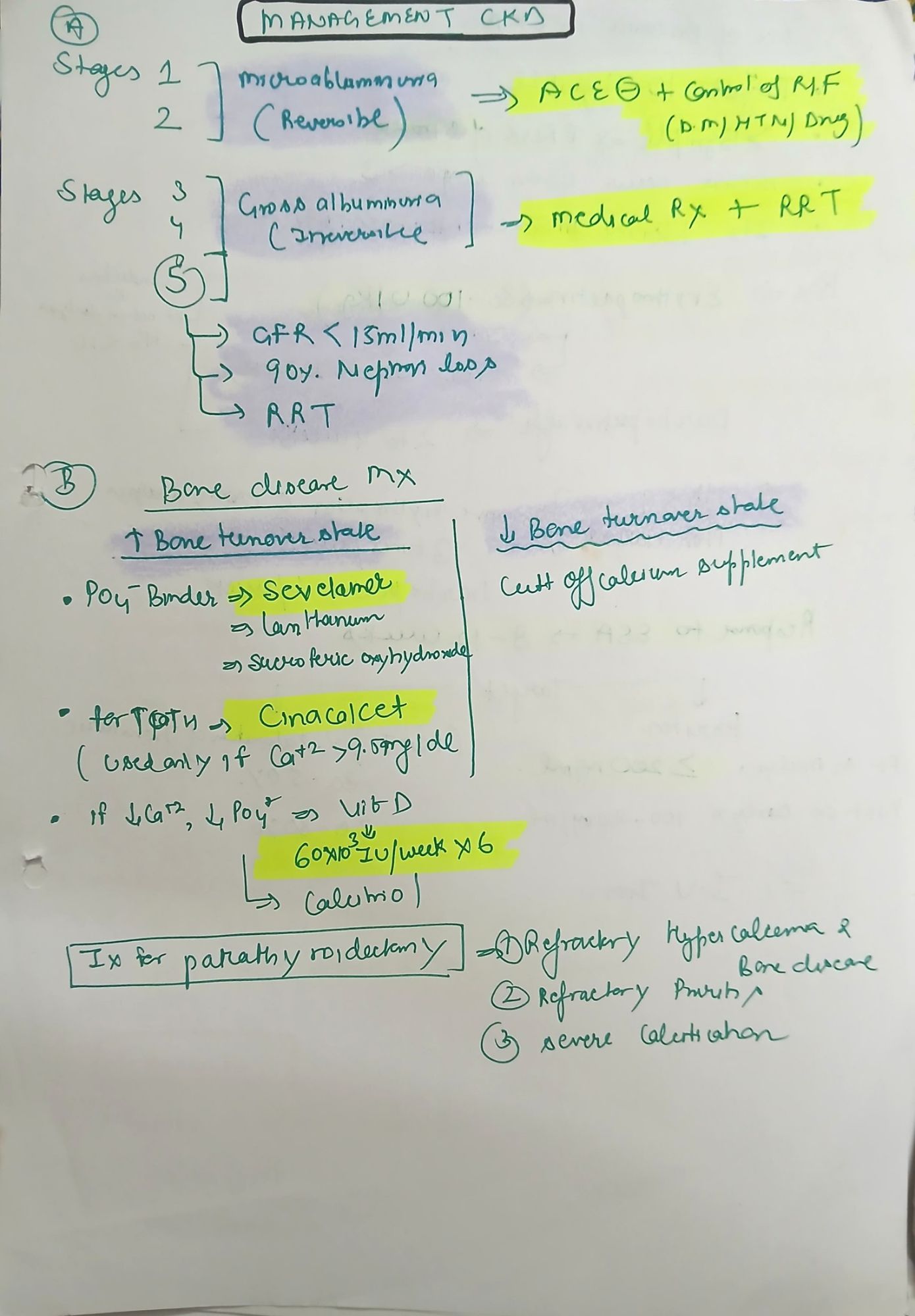
🦴 CKD-MBD (Bone Disease)
- Hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, ↑ PTH → bone resorption
- Treatment:
- Phosphate binders: Sevelamer, calcium acetate
- Vitamin D analogs: Calcitriol (0.25–1 mcg/day)
- Calcimimetics: Cinacalcet for high PTH
⚡️ Hyperkalemia in CKD
- Causes: ↓ excretion, RAS inhibitors, acidosis, diet
- Treatment:
- Calcium gluconate 10 mL IV over 5–10 min
- Insulin + 25–50 mL Dextrose 50%
- Salbutamol neb
- Furosemide IV
- Dialysis if severe/refractory
💧 Fluid & Electrolyte Management
- Use balanced crystalloids if needed
- Monitor Na, K, HCO₃ daily
- Be cautious with volume overload; loop diuretics as needed
🚨 When to Refer to Nephrology
- GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Rapid progression (decline >5 mL/min/year)
- Refractory hypertension, hyperkalemia, acidosis
- Suspected glomerulonephritis
- ESRD planning (dialysis, transplant)
🏥 When to Start Dialysis in CKD
Based on clinical criteria, not just GFR:
“AEIOU” mnemonic:
- A: Metabolic Acidosis
- E: Electrolyte (esp. K⁺) imbalance
- I: Intoxications (e.g., lithium)
- O: Volume Overload
- U: Uremic symptoms (encephalopathy, pericarditis)
💊 Drugs in Renal Failure: What’s Safe, What’s Not
✅ Category 1: Generally SAFE (No Adjustment Needed)
|
Drug Class |
Examples |
|
Analgesics |
Acetaminophen (paracetamol) |
|
Antibiotics |
Ceftriaxone, Clindamycin, Azithromycin, Doxycycline |
|
Cardiac drugs |
Amlodipine, Metoprolol, Diltiazem |
|
GI drugs |
PPIs (omeprazole), Antacids (non-Mg-based), Domperidone |
|
Endocrine |
Insulin (but monitor), Glipizide (short-acting sulfonylurea) |
|
Antiepileptics |
Valproate, Carbamazepine, Levetiracetam (monitor levels) |
|
Anticoagulants |
Warfarin, Unfractionated Heparin (UFH) |
|
Miscellaneous |
Lorazepam, Haloperidol, Prednisolone |
⚠️ Even “safe” drugs may need monitoring for efficacy or toxicity, especially in ESRD or dialysis patients.
⚖️ Category 2: REQUIRES DOSE ADJUSTMENT
|
Drug Class |
Examples |
Notes |
|
Beta-lactam antibiotics |
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems |
Adjust based on GFR |
|
Aminoglycosides |
Gentamicin, Amikacin |
Risk of nephrotoxicity; monitor trough levels |
|
Fluoroquinolones |
Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin |
Risk of seizures if unadjusted |
|
Vancomycin |
— |
TDM essential |
|
LMWH |
Enoxaparin |
Anti-Xa monitoring preferred in ESRD |
|
Anti-TB drugs |
Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide |
INH & Rifampin are usually safe |
|
Oral Hypoglycemics |
Sitagliptin, Gliclazide |
Dose based on eGFR |
|
Antivirals |
Acyclovir, Tenofovir |
Risk of crystal nephropathy |
|
Antifungals |
Fluconazole, Amphotericin B (liposomal preferred) |
Adjust fluconazole; amphotericin = nephrotoxic |
|
Digoxin |
— |
High risk of toxicity; adjust & monitor levels |
|
Allopurinol |
— |
Risk of toxicity (SJS/TEN) in CKD |
|
Gabapentinoids |
Gabapentin, Pregabalin |
Accumulate in CKD → CNS side effects |
|
Metformin |
— |
Safe if GFR >30; stop during AKI/contrast exposure |
❌ Category 3: AVOID or USE WITH EXTREME CAUTION
|
Drug Class |
Examples |
Why? |
|
NSAIDs |
Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin |
↓ GFR, risk of AIN/ATN |
|
ACEi/ARBs |
Enalapril, Losartan |
Use cautiously in AKI, bilateral RAS |
|
Potassium-sparing diuretics |
Spironolactone, Amiloride |
Hyperkalemia risk |
|
Certain oral hypoglycemics |
Glyburide (glibenclamide) |
Prolonged hypoglycemia |
|
Magnesium-based antacids |
— |
Risk of hypermagnesemia |
|
Nitrofurantoin |
— |
Ineffective + toxicity in low GFR |
|
Metformin (GFR <30) |
— |
Risk of lactic acidosis |
|
Contrast media |
Iodinated contrast |
Risk of contrast-induced nephropathy |
|
Bisphosphonates |
Zoledronate |
Avoid in CrCl <30 mL/min |
|
Colchicine |
— |
Neurotoxicity risk in ESRD |
|
Lithium |
— |
Excreted by kidneys, narrow therapeutic index |